How to make a Morse Encoder
What you will learn:
In this tutorial, we will go through the explanation of the Morse encoder algorithm and its encapsulation into a Luos service. Finally we will see, using examples, how we can exploit the output of the encoder algorithm, and how we can generate and share an input to be encoded by the application.
Part 1: Morse encoder algorithm
1. Introduction
The first step of this tutorial is to create the application service that will encode words into Morse signals. The final goal will be to generate an output that will be the translation of an input word into Morse code.
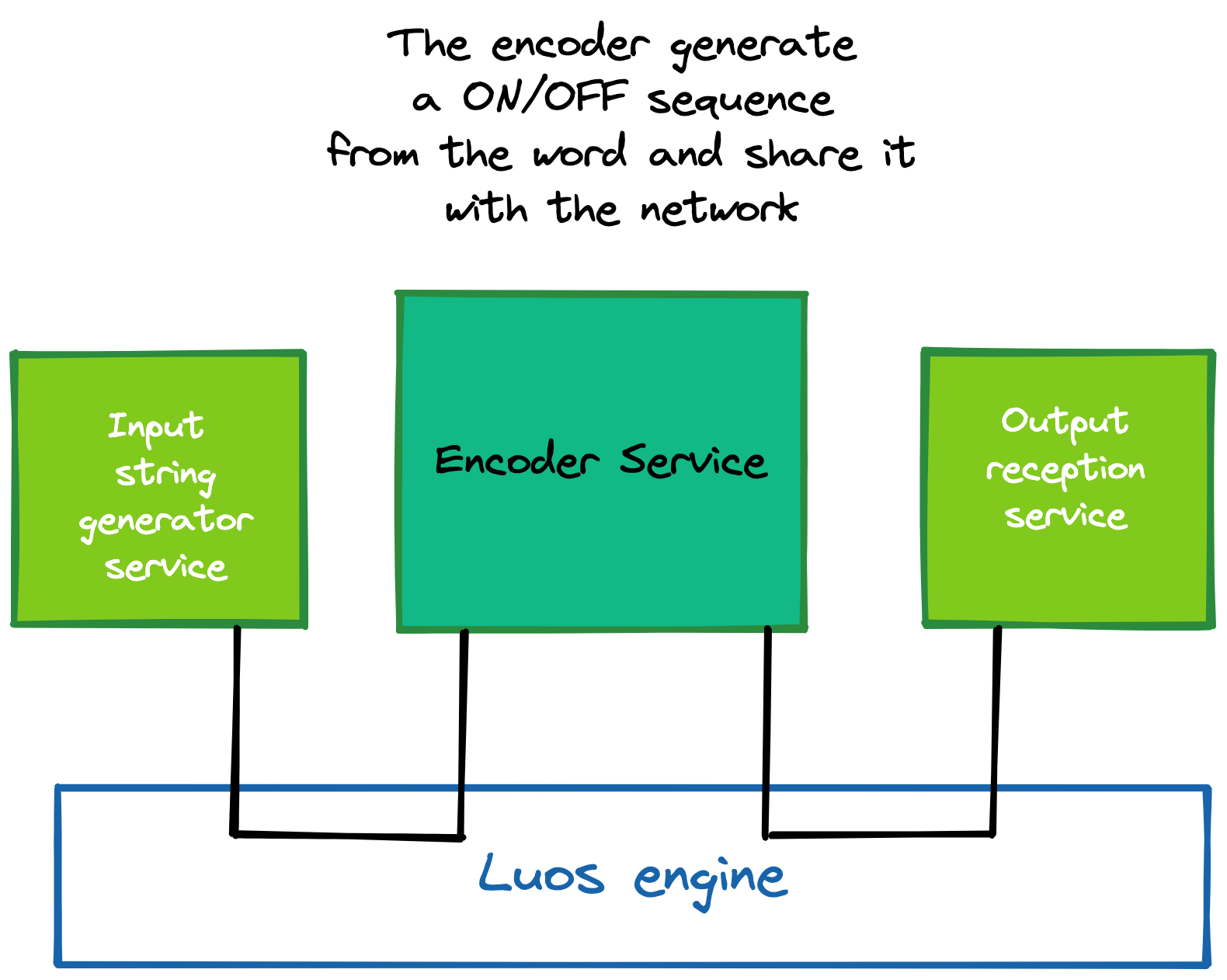
2. A Morse encoder principle
The principle of a Morse coder is to translate a character into Morse code represented by a succession of dots and dashes, which is an high level state on a Morse line during a certain time.
Words are cut in letters, and letters are cut in a succession of Morse encoded elements.
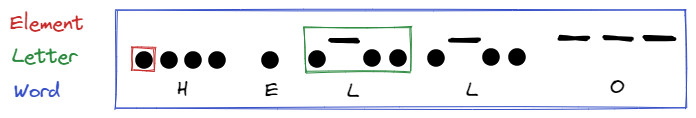

In this application:
- A word = 10 letters buffer
- A letter = 10 elements buffer
- An element = state information (0 or 1) and time information (short state = ".", long state "-")
- short state = state once to 1
- long state = state 3 times to 1
- between each element = state once to 0
- between each letter = state 3 times to 0
- between each word = state 7 times to 0
3. Encoder application operation
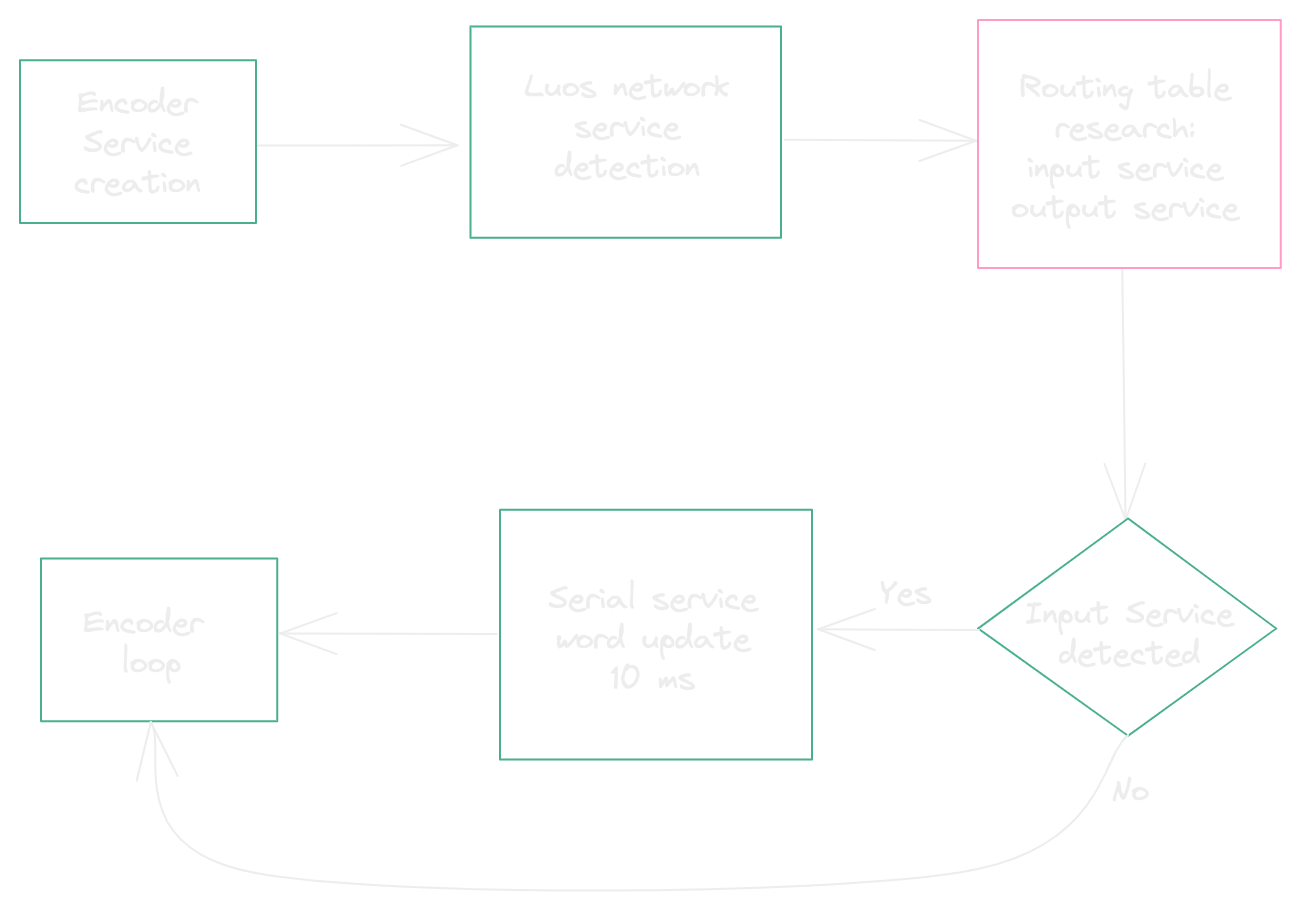
First of all, we will create a new Luos service. A Luos service can be a driver or an application (or app). Here we need to create an application that will contain not only an algorithm that encodes strings into Morse sequences, but also the logic to handle the link among the Luos drivers which will be integrated afterwards.
A Luos application doesn't depend on any hardware. It can be uploaded on any board without changing anything. Applications contains a piece of the “logic” of your project. As opposing to driver services, a Luos application can find and take the initiative to send messages to another service.
Like any Luos services, The encoder app has 3 functions:
- Init
- Loop
- Message handler
Init:
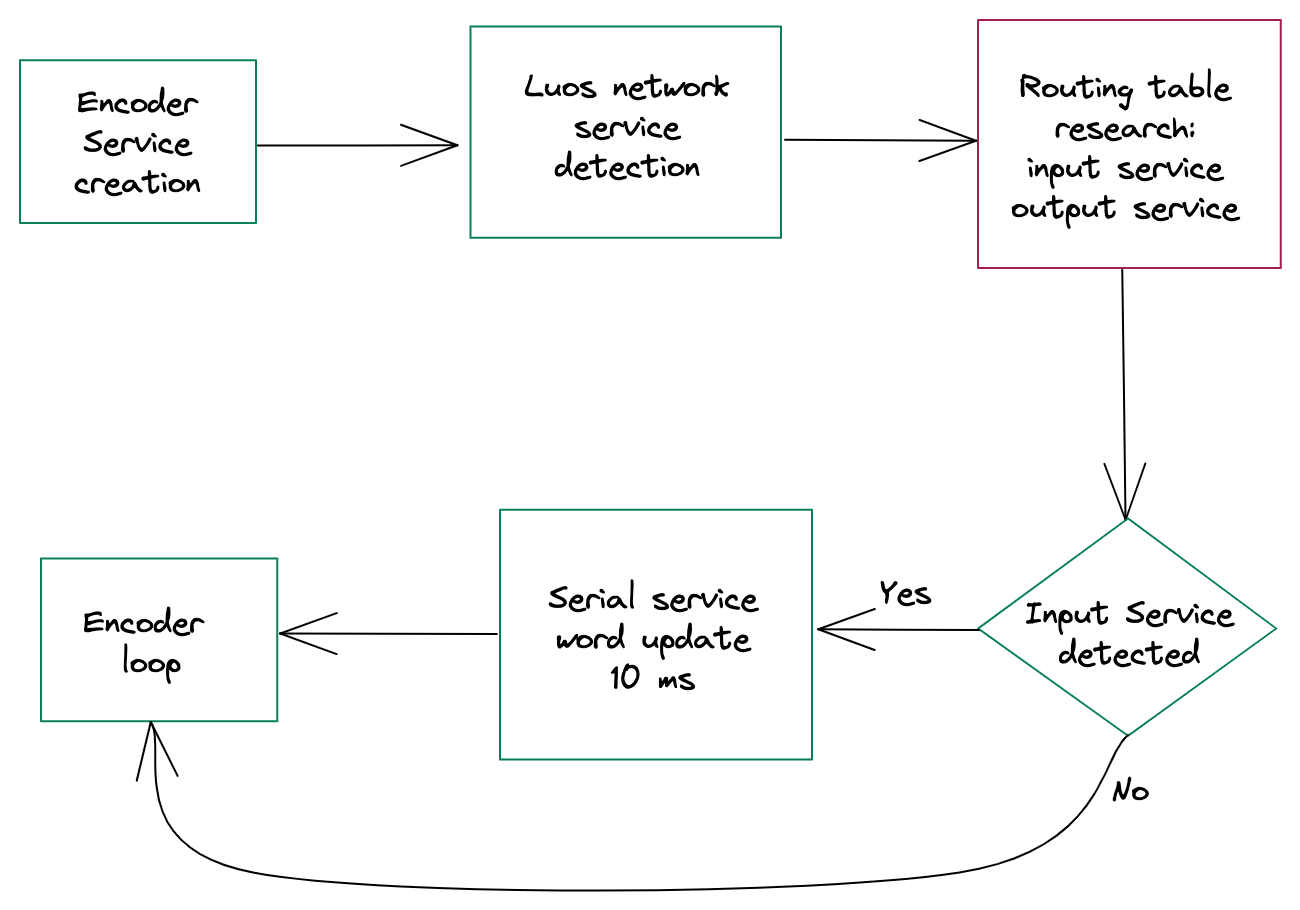
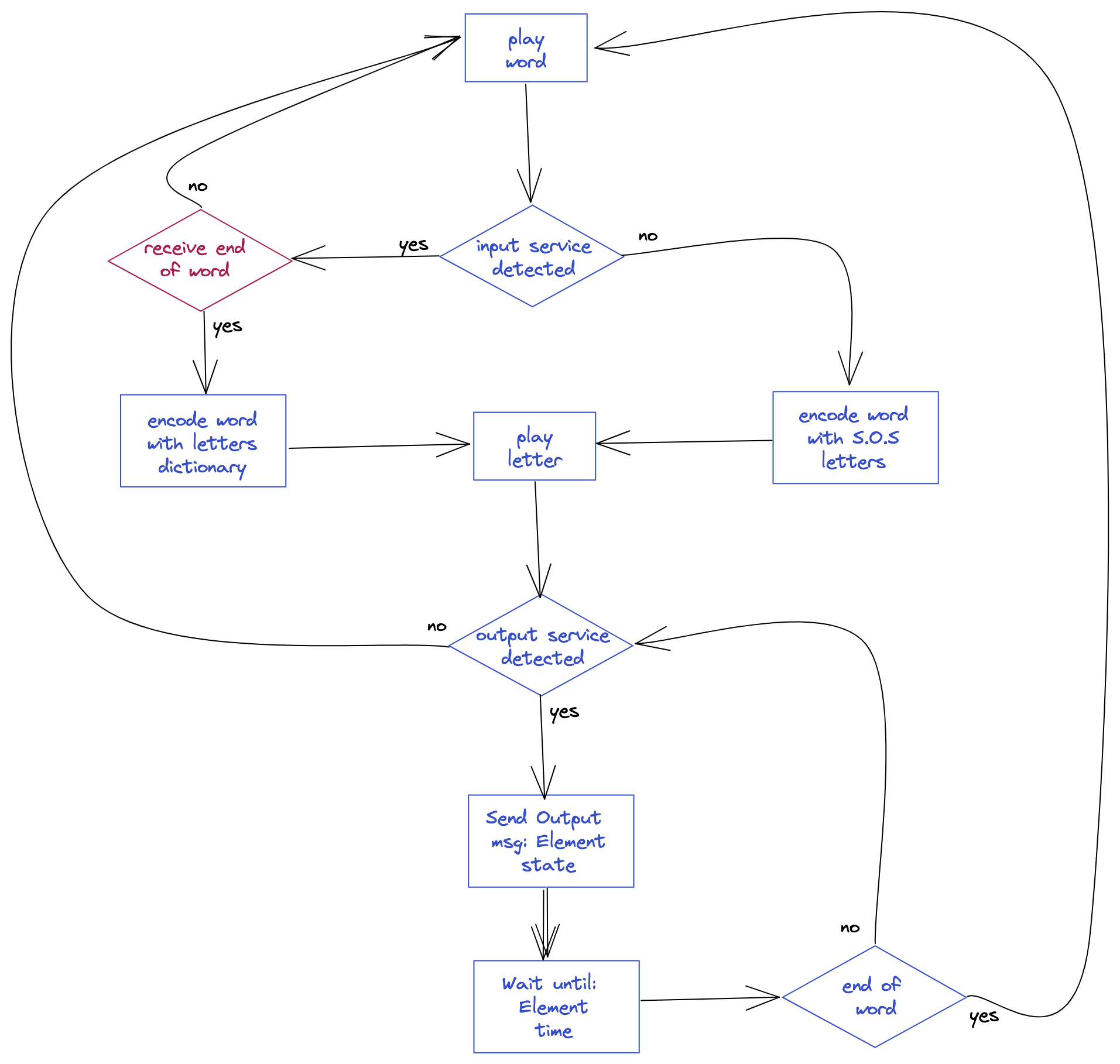
Loop:
First, clone or download this project and open it with VSCode:

Next, let's enter into the details of the application for a better understanding...
4. Encoder's main feature
a. Detection
Our service will have two operating modes:
- Start a detection, an input service is detected, create an output of the Morse words received from it.
- If no input service detected, it will play the S.O.S sequence (
... --- ...).
void Encoder_Init(void)
{
// service initialization
revision_t revision = {.major = 1, .minor = 0, .build = 0};
// Service creation following state profile
service = Luos_CreateService(Encoder_MsgHandler, LUOS_LAST_TYPE, "encoder_service", revision);
// Detect all services of your network and create a routing_table
Luos_Detect(service);
// initialize variables
morse_state = false;
morse_period = 0;
morse_start_timeout = 0;
element_index = 0;
letter_index = 0;
end_of_letter = true;
end_of_word = true;
}
All services have to be connected to the Luos network to send and receive messages. For services to be connected and recognized in the network, we have to launch a detection.
Luos_Detect() launches the detection and its end can be detected with Luos_IsNodeDetected(): once the node is connected, the function returns TRUE. After that, all services can send and receive messages.
We also added some initialization code to set default values for variables.
b. Play a word
MorseWord receive_word;
MorseWord sos_table = {
.morse_letter[0] = &s_letter,
.morse_letter[1] = &o_letter,
.morse_letter[2] = &s_letter,
.morse_letter[3] = &end_letter,
.morse_letter[4] = &end_word_marker,
};
bool input_detected = false;
/******************************************************************************
* @brief loop must be call in project loop
* @param None
* @return None
******************************************************************************/
void Encoder_Loop(void)
{
if (Luos_IsNodeDetected())
{
if (input_detected)
{
Encoder_PlayWord(&receive_word);
}
else
{
end_of_word = false;
Encoder_PlayWord(&sos_table);
}
}
}
Notice that we use Luos_IsNodeDetected(): this function checks if the node is connected on the Luos network. We use this function to prevent running the service loop function if the node is not connected.
5. Encoder message handler
Pay attention to the second if() statement: here we use the END_DETECTION message received at the end of the detection process to set the input_detected variable.
Also, after the END_DETECTION message, we do a research into the routing table.
The routing table is a structure that has all the information about the nodes and services that exist in a system. Each service can recognize the characteristics of the others by filtering the data of the routing table, and find the services that it wants to communicate with.
/******************************************************************************
* @brief manage messages send to the service
* @param Service which send the message
* @param msg which send the message
* @return None
******************************************************************************/
void Encoder_MsgHandler(service_t *service, msg_t *msg)
{
uint16_t index = 0;
uint8_t received_letter = 0;
if (msg->header.cmd == SET_CMD)
{
while (msg->data[index] != '\r')
{
receive_word.morse_letter[index] = Encoder_DecodeLetter(msg->data[index]);
index += 1;
}
receive_word.morse_letter[index] = &end_letter;
receive_word.morse_letter[index + 1] = &end_word_marker;
end_of_word = false;
end_of_letter = false;
}
if (msg->header.cmd == END_DETECTION)
{
search_result_t result;
RTFilter_Type(RTFilter_Reset(&result), STATE_TYPE);
output_id = result.result_table[0]->id;
RTFilter_Type(RTFilter_Reset(&result), PIPE_TYPE);
if (result.result_nbr > 0)
{
time_luos_t update_time = 0.01;
msg_t update_msg;
update_msg.header.target = result.result_table[0]->id;
update_msg.header.target_mode = IDACK;
TimeOD_TimeToMsg(&update_time, &update_msg);
update_msg.header.cmd = UPDATE_PUB;
Luos_SendMsg(service, &update_msg);
input_detected = true;
return;
}
input_detected = false;
}
}
In the first if() statement, notice that we created a specific CMD to manage this data. It is used to filter messages in the handler and process only this type of messages.
We receive an array filled with letters to encode and we iterate on this array to encode each letter. We can detect the end of the word with the character \r.
6. Change output state with Luos message
We create a Morse sequence from letters, and send them as outputs to the Luos network:
void Encoder_SendMorse(bool state)
{
// Now send a message
if (output_id > 0)
{
msg_t output_msg;
output_msg.header.target = output_id ;
output_msg.header.cmd = IO_STATE;
output_msg.header.target_mode = IDACK;
output_msg.header.size = sizeof(char);
output_msg.data[0] = state;
Luos_SendMsg(service, &output_msg);
}
}
The argument state is used to send ON/OFF to the output service, then we create a msg_t variable which will be filled with needed information.
Once the message is created we can send it with the Luos_SendMsg() function.
7. Element and dictionnary
We will use this function to create Morse sequences for each letter in the alphabet. In Morse, each letter can be broken down in several ON/OFF states; the duration of these states is defined in the Morse code's Wikipedia article.
/*******************************************************************************
* Definitions
******************************************************************************/
#define SHORT_PERIOD 300
typedef enum WordLength
{
SHORT = SHORT_PERIOD,
LONG = 3 * SHORT_PERIOD,
WORD_SPACE = 7 * SHORT_PERIOD,
} WordLength;
typedef struct MorseElement
{
union
{
struct
{
uint16_t state;
uint16_t word_length;
};
uint32_t value;
};
} MorseElement;
typedef struct MorseLetter
{
union
{
MorseElement morse_element[10];
uint32_t value;
};
} MorseLetter;
Use the file dictionnary to encode characters into Morse sequences exemple:
/******************************************************************************
* @file dictionnary
* @brief morse dictionnary
* @author Luos
* @version 0.0.0
******************************************************************************/
#ifndef DICTIONNARY_H
#define DICTIONNARY_H
#include "encoder.h"
/*******************************************************************************
* Definitions
******************************************************************************/
#define LETTER_END 0xFFFFFFF1
/*******************************************************************************
* Variables
******************************************************************************/
MorseLetter a_letter = {
.morse_element[0] = {.state = true, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[1] = {.state = false, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[2] = {.state = true, .word_length = LONG},
.morse_element[3] = {.state = false, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[4].value = LETTER_END,
};
MorseLetter b_letter = {
.morse_element[0] = {.state = true, .word_length = LONG},
.morse_element[1] = {.state = false, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[2] = {.state = true, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[3] = {.state = false, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[4] = {.state = true, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[5] = {.state = false, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[6] = {.state = true, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[7] = {.state = false, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[8].value = LETTER_END,
};
MorseLetter c_letter = {
.morse_element[0] = {.state = true, .word_length = LONG},
.morse_element[1] = {.state = false, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[2] = {.state = true, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[3] = {.state = false, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[4] = {.state = true, .word_length = LONG},
.morse_element[5] = {.state = false, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[6] = {.state = true, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[7] = {.state = false, .word_length = SHORT},
.morse_element[8].value = LETTER_END,
};
...
8. Play a Morse letter and word
When a complete word is received (/r), Encoder_PlayWord() will use the function Encoder_PlayLetter() to change the state of the output depending on the element (1 or 0), and wait the right time depending on the element ("." or "-").
void Encoder_PlayLetter(MorseLetter *letter)
{
// for each element in a letter
if ((letter->morse_element[element_index].value != LETTER_END) & !end_of_letter)
{
if (Luos_GetSystick() - morse_start_timeout > morse_period)
{
morse_state = letter->morse_element[element_index].state;
morse_period = letter->morse_element[element_index].word_length;
// send new output state
Encoder_SendMorse(morse_state);
// wait for the time period
morse_start_timeout = Luos_GetSystick();
// go to the next element
element_index += 1;
}
}
else
{
// reset element index and go to the next letter
element_index = 0;
end_of_letter = true;
}
}
Next step
Here we are, we finished the encoder service. The next step is to get the encoder output and use a Luos service to display it.
In the final step, we will generate input words so that we could send our own words, to encode them in Morse code.

